Anatomy of Cannabis: Difference between revisions
(→Buds: Added diagram) |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==Buds== |
==Buds== |
||
| + | [[File:Bud anatomy.png|thumb|346x346px]] |
||
| + | |||
==== Cola ==== |
==== Cola ==== |
||
| − | A cluster of many buds on the top of a stem. Colas will appear and become larger throughout the flowering stage |
+ | A cluster of many buds on the top of a stem. Colas will appear and become larger throughout the [[Life Stages#Flowering|flowering stage]]. |
==== Trichromes ==== |
==== Trichromes ==== |
||
| Line 44: | Line 46: | ||
====Stigma==== |
====Stigma==== |
||
| − | Hair-like structures that emerge from the bud often (confusingly) referred to as Pistils. This is most likely because stigma possessing female plants are referred to as pistillate, which then became short-hand. |
+ | Hair-like structures that emerge from the bud often (confusingly) referred to as Pistils. This is most likely because stigma possessing female plants are referred to as pistillate, which then became short-hand. The colouration of the stigma can provide some insight into the maturity of the plant, as the plant matures, the stigma turn from white to orange. |
| − | The colouration of the stigma can provide some insight into the maturity of the plant, as the plant matures the stigma turn from white to orange. |
||
| − | ====Bract==== |
+ | ====Calyx (Bract)==== |
The first part of the flower that forms, the Bract provides protection for the pistils and stigma and is the most resinous part of the bud. |
The first part of the flower that forms, the Bract provides protection for the pistils and stigma and is the most resinous part of the bud. |
||
Revision as of 20:24, 12 March 2022
Knowledge of the proper name for each part of the Cannabis plant can help one describe problems with a cultivar.
Leaves
Types of leaf
Cotyledons
Technically not "true" leaves, these are the initial pair of "leaves" that are present inside the seed casing.
Sugar leaves
Small leaves with trichomes that grow from the buds. They are trimmed before the bud is smoked, either before or after drying.
Fan leaves
The largest leaves on the plant dedicated to photosynthesis. In a healthy plant, the fan leaves will have up 7 or even 9 fingers.
Parts of the leaf
Petiole
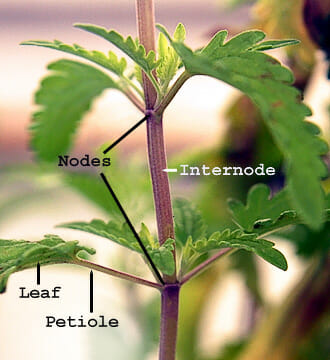
The stalk connecting the leaf to the stem.
Apex
The pointed tip of a fan leaf.
Ventral surface
Upper side of the leaf.
Dorsal surface
The under side of a leaf.
Margin
The outer perimeter or edge of a leaf.
Stomata
Stomata are tiny pores in the plant tissue that allow for gas exchange. The majority can be found on the underside of the leaves but they are also found on the surface of leaves and stems.
Buds
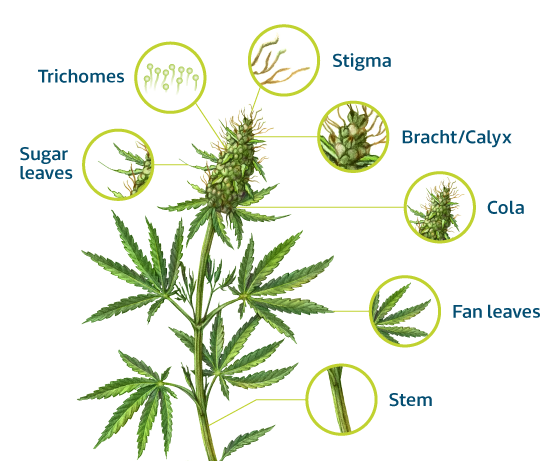
Cola
A cluster of many buds on the top of a stem. Colas will appear and become larger throughout the flowering stage.
Trichromes
Trichomes are resin-filled glands that appear on the sugar leaves and buds of Cannabis in the flowering stage. They contain THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids. They first appear on the plant as a translucent colour but slowly turn milky white as the plant matures. The opacity indicates the amount of THC in the trichrome. As flowering continues the milky white colour turns to amber as the THC converts into CBD.
Terpenes
Organic compounds found in the highest concentration in buds that create the taste and aroma of Cannabis.
Stigma
Hair-like structures that emerge from the bud often (confusingly) referred to as Pistils. This is most likely because stigma possessing female plants are referred to as pistillate, which then became short-hand. The colouration of the stigma can provide some insight into the maturity of the plant, as the plant matures, the stigma turn from white to orange.
Calyx (Bract)
The first part of the flower that forms, the Bract provides protection for the pistils and stigma and is the most resinous part of the bud.
Plant body
Node
Points on the steam where lateral branches grow from the main stem. The third node is where the plant begins to develop strong bud producing branches.[citation needed]
Plant metrics
Inter-nodal distance
Distance between nodes on the main stem.
Stem diameter
This refers to the diameter of the main stem. It has been shown that stem diameter is positively correlated with weight yield.